Earthquake Scale
Earthquake magnitude is a measure of the size or amplitude of the seismic waves generated by an earthquake source and recorded by seismographs.
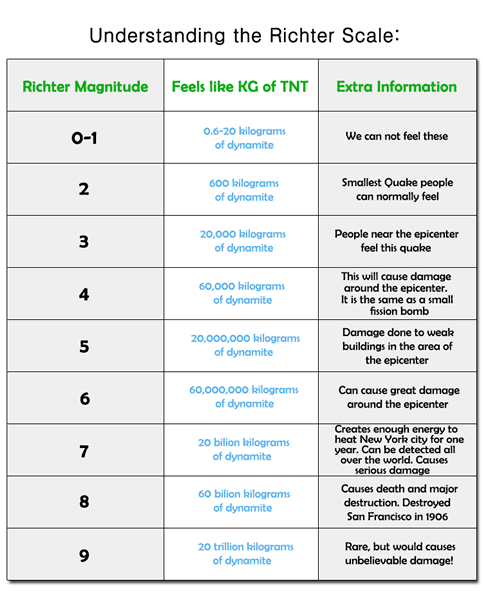
Earthquake scale. Often felt but. Earthquake size as measured by the richter scale is a well known but not well understood concept. The richter scale also called the richter magnitude scale or richter s magnitude scale is a measure of the strength of earthquakes developed by charles f.
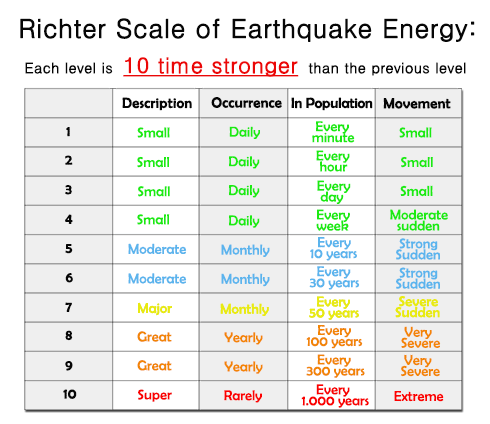
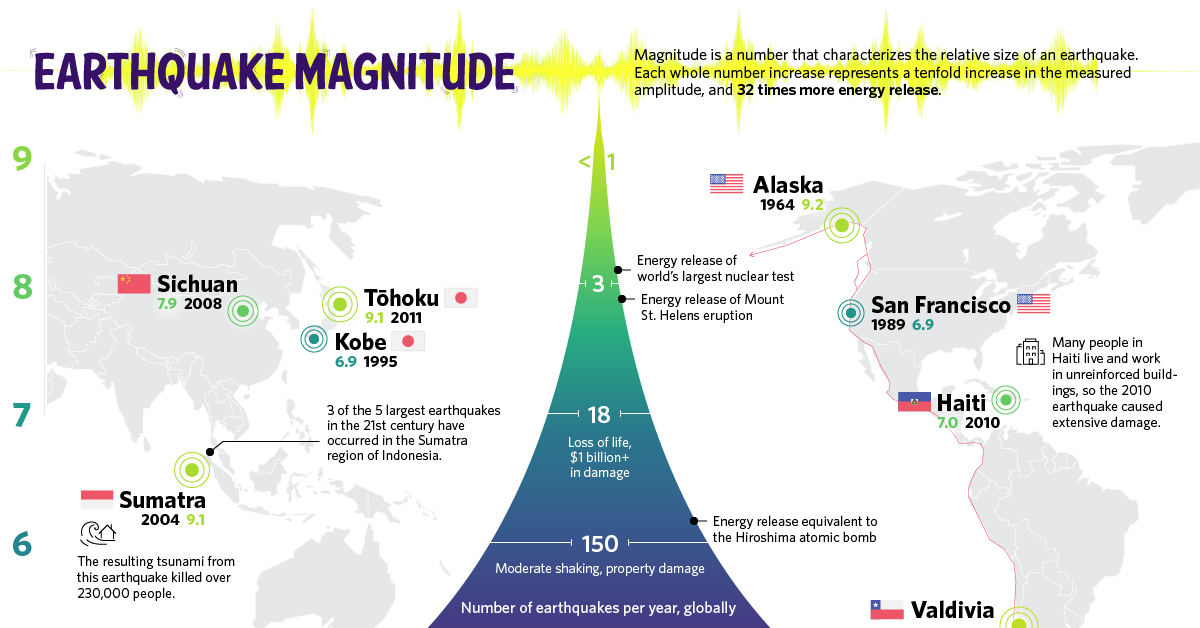
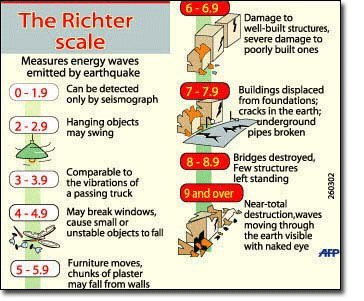
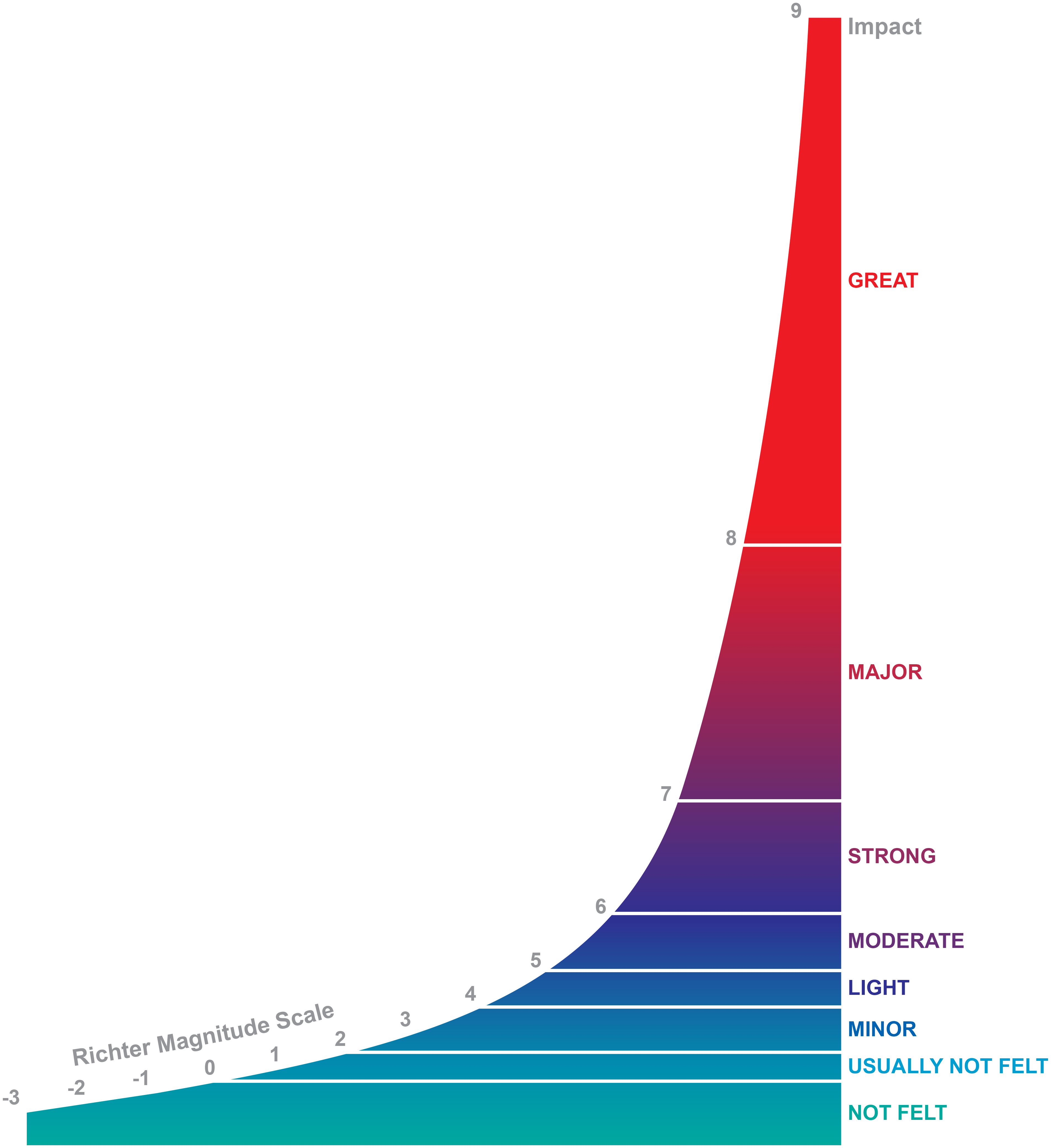
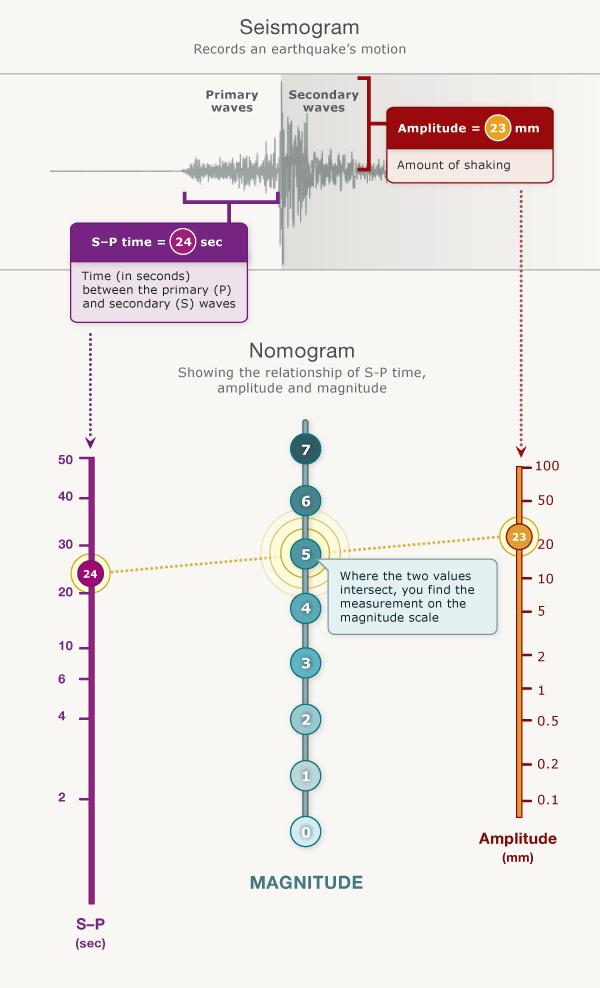
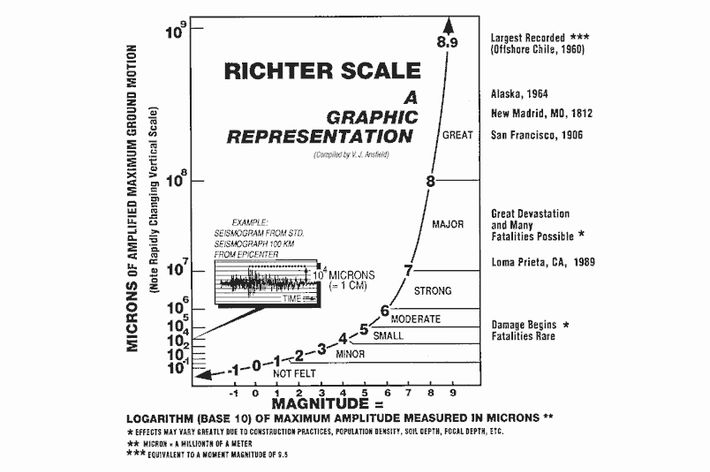
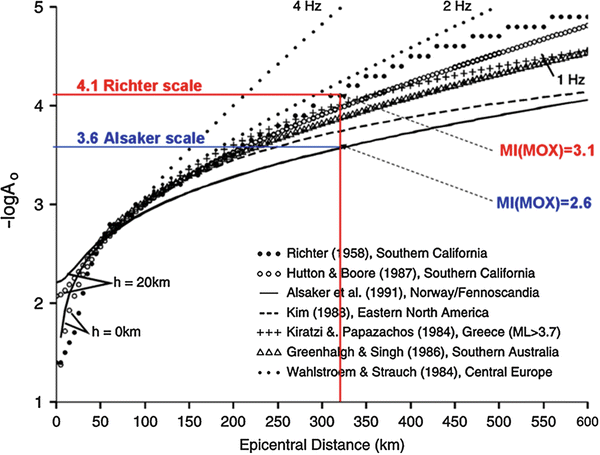
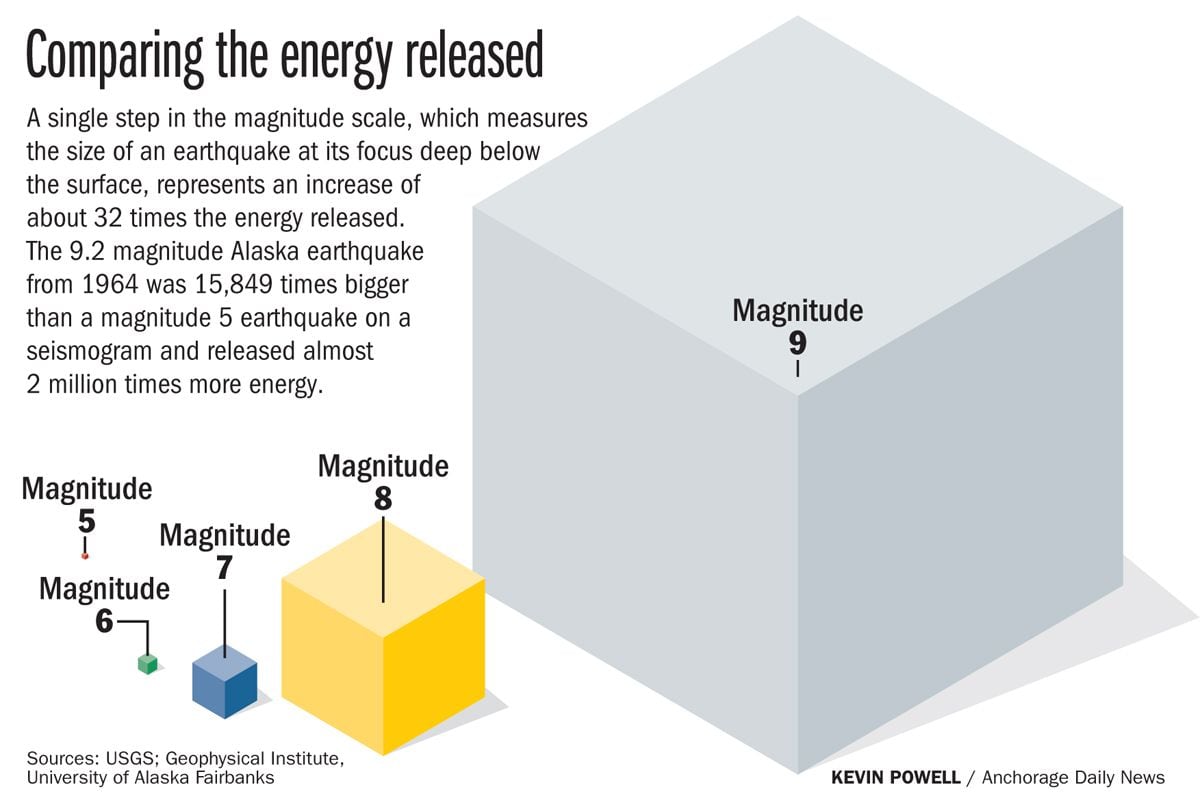
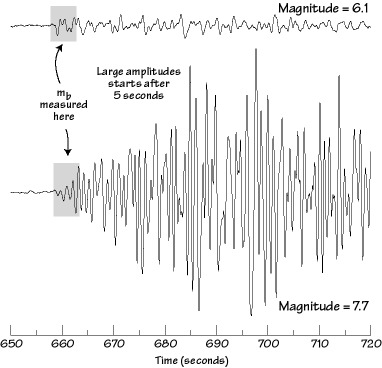
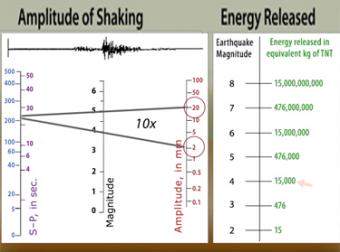
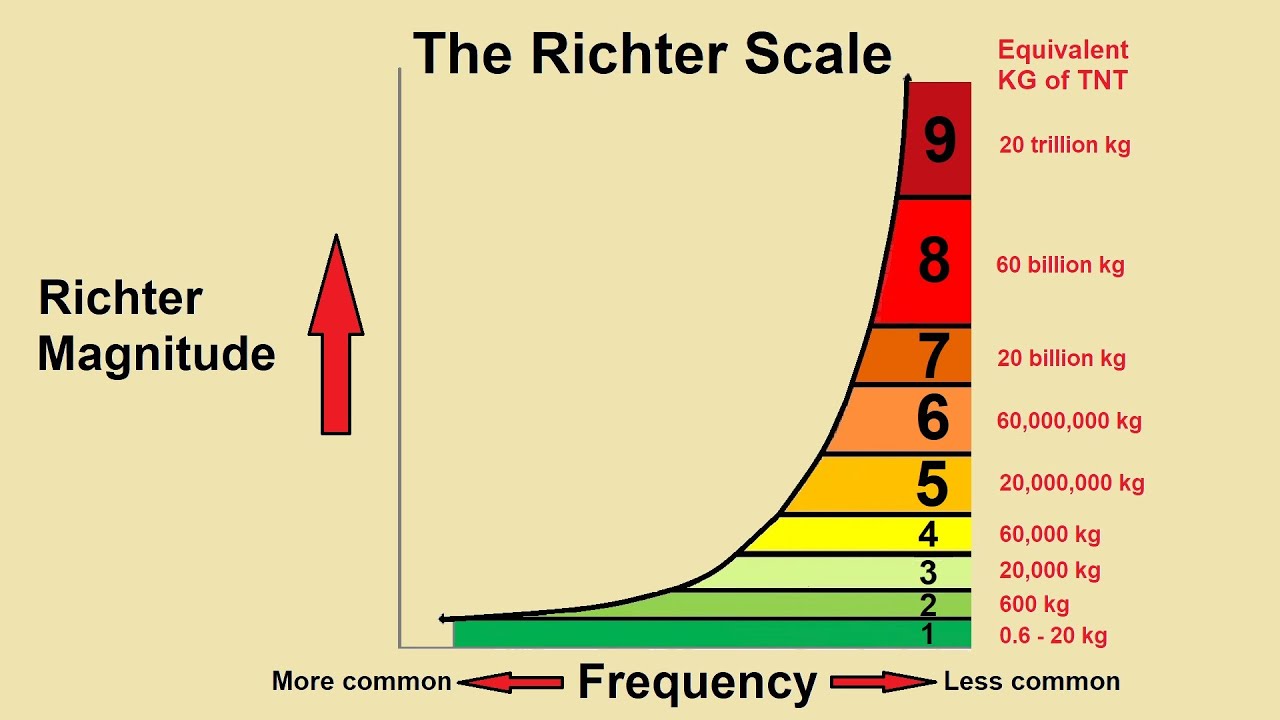
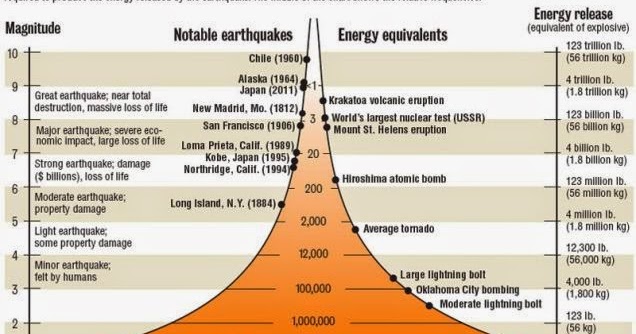
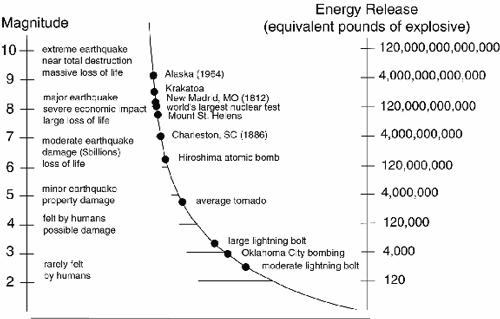
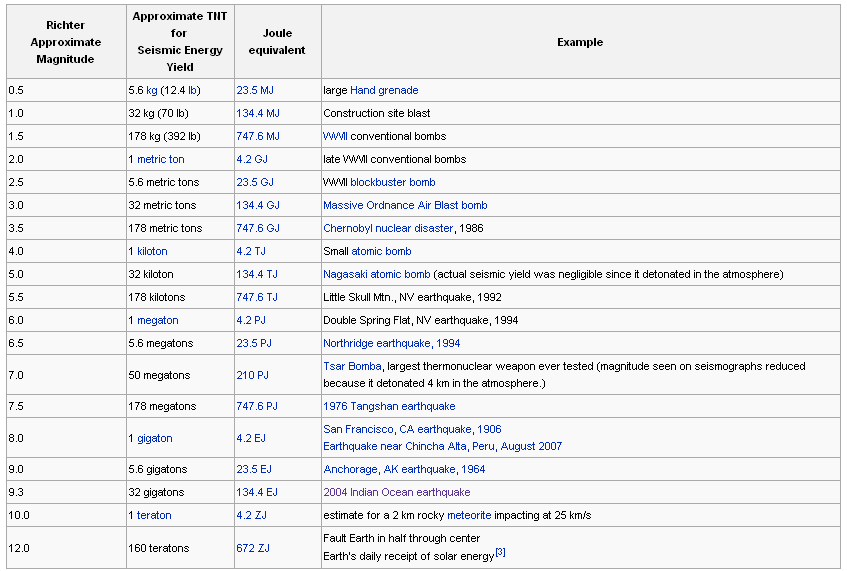
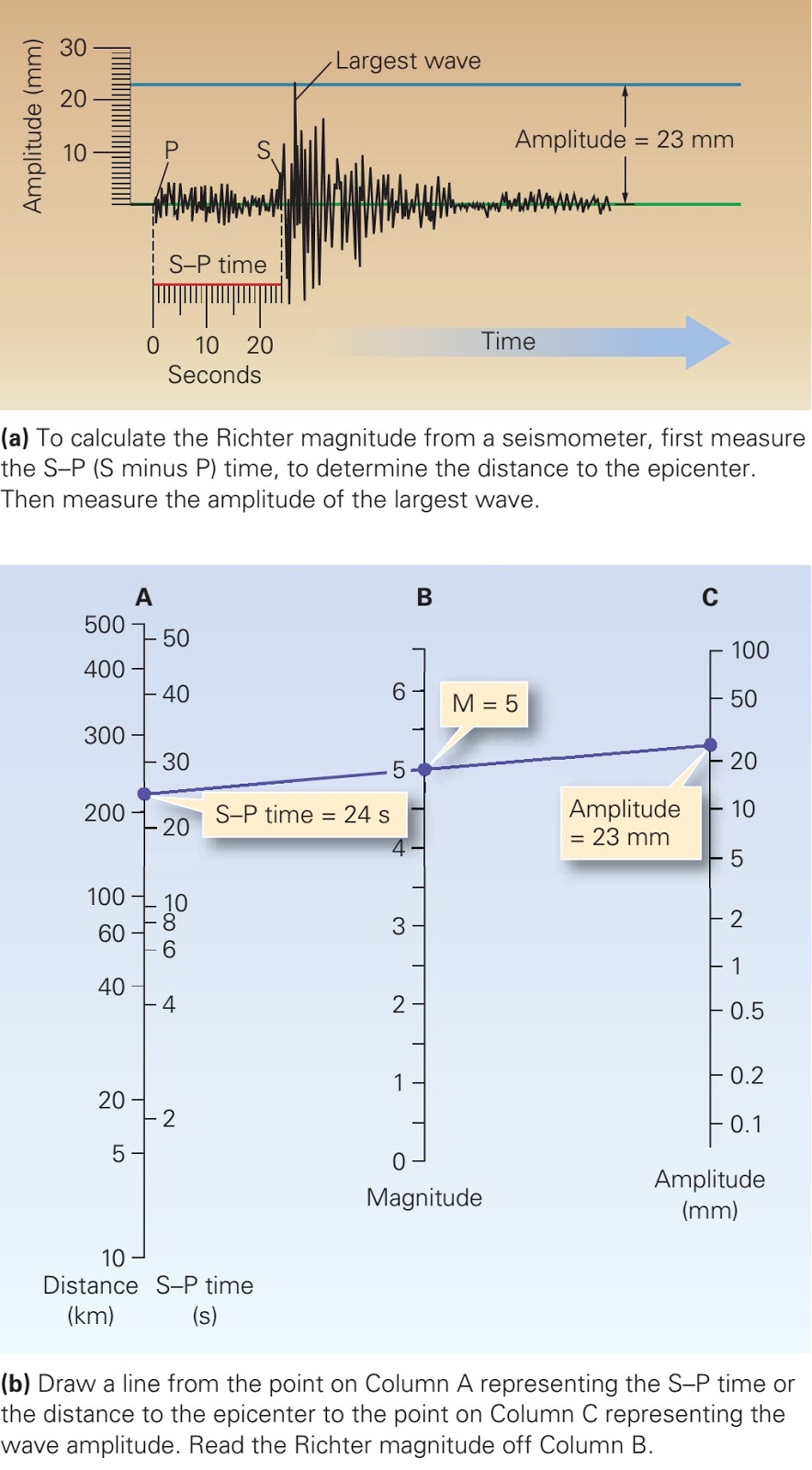
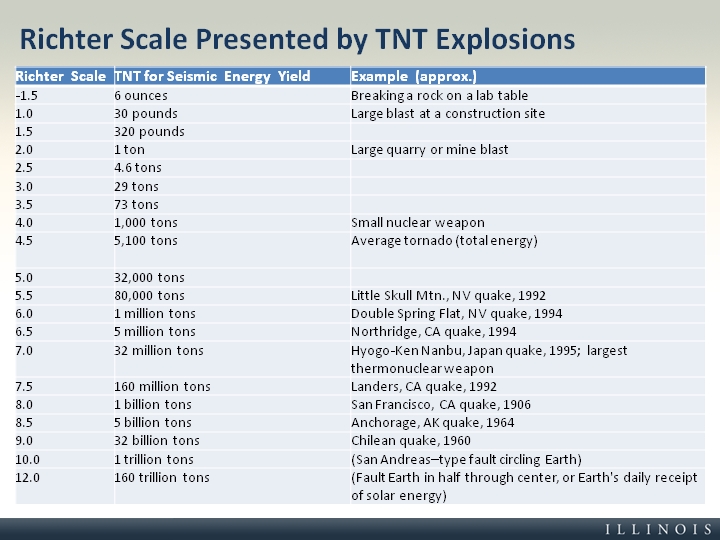
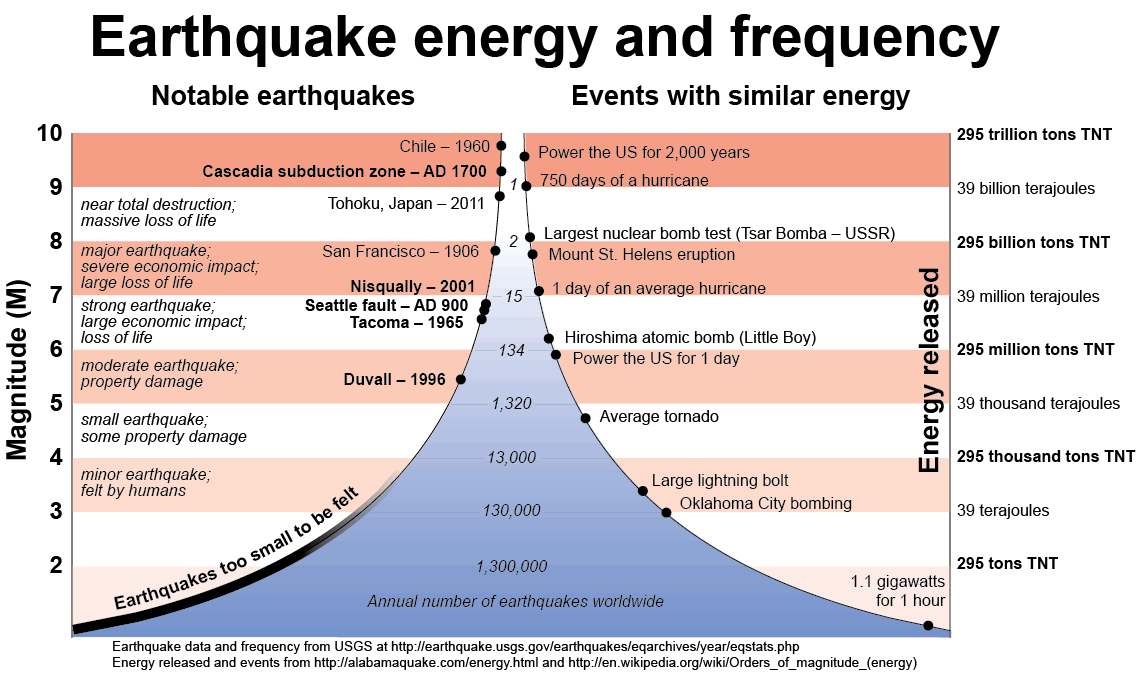
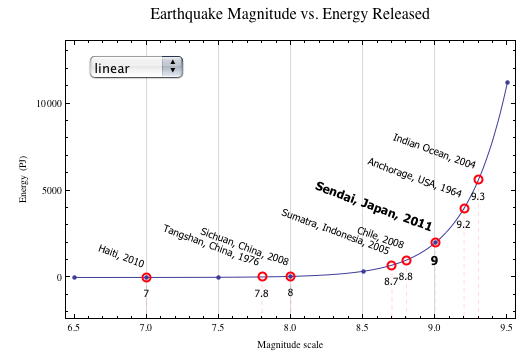
The richter scale is logarithmic meaning that whole number jumps indicate a tenfold increase in this case the increase is in wave amplitude. Thus the increase is a degree of magnitude of the 32 fold increase in the released seismic energy. Magnitude is determined using the logarithm of the amplitude height of the largest seismic wave calibrated to a scale by a seismograph.
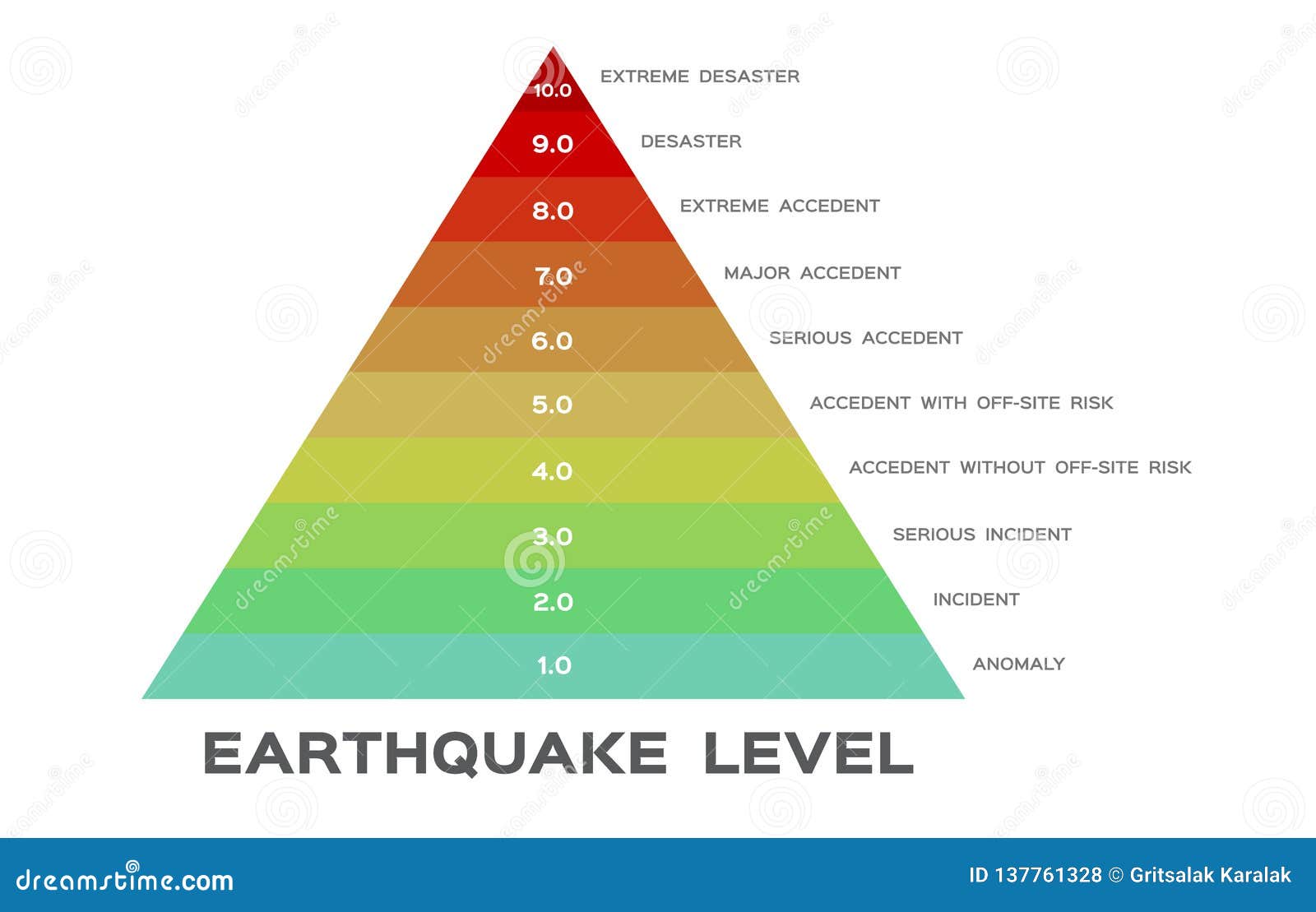
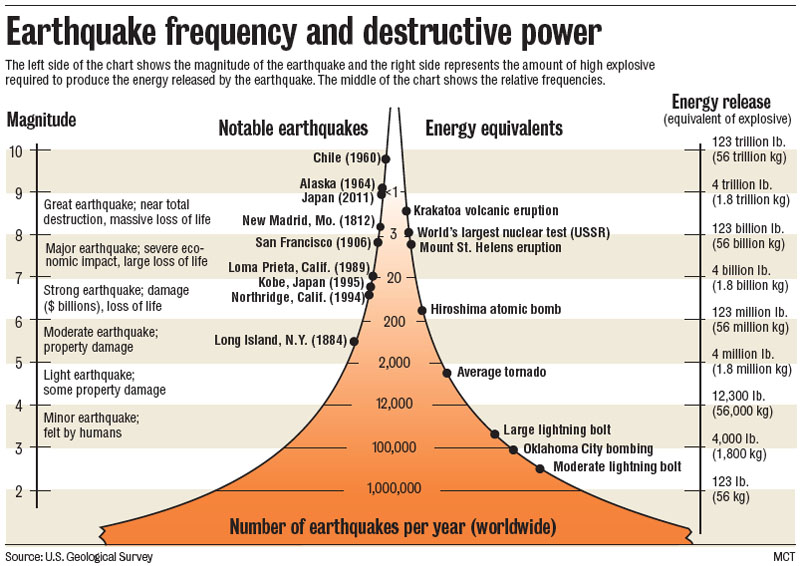
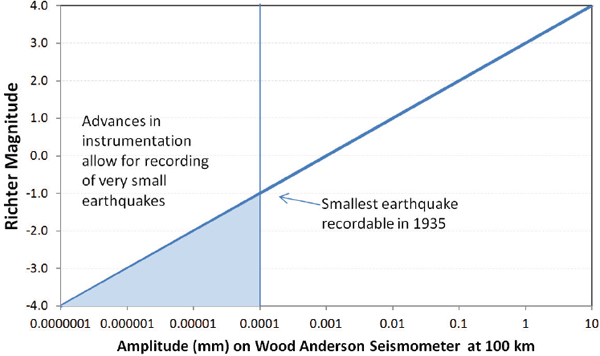
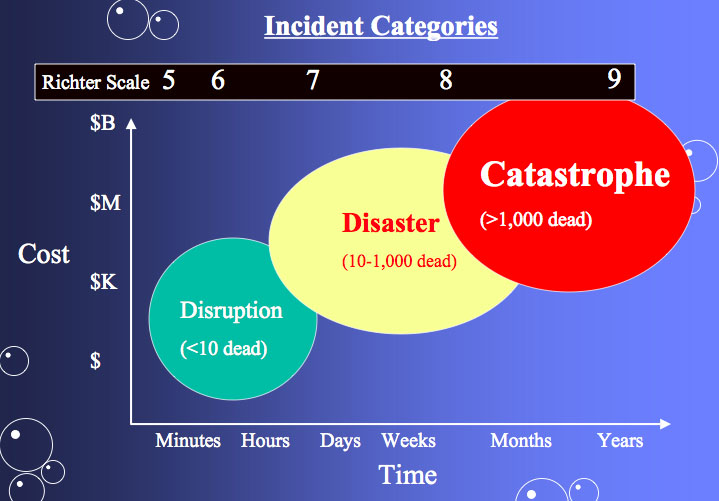
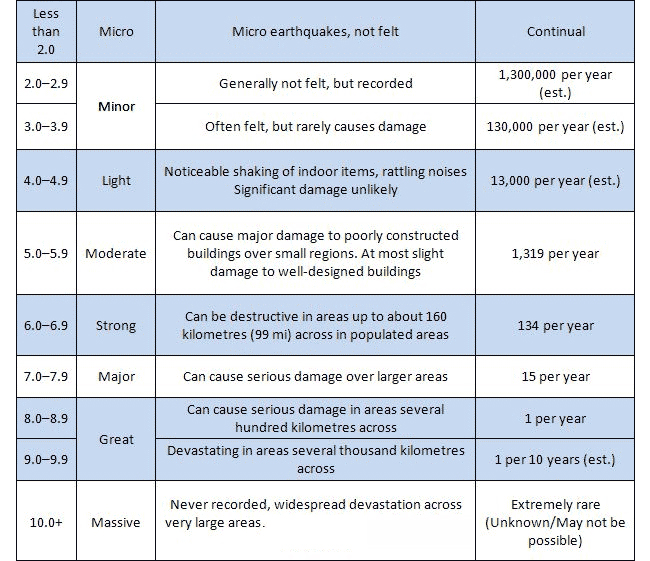
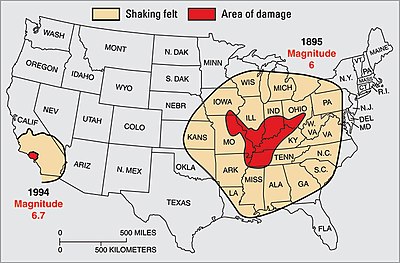
An earthquake of magnitude 2 is subtle until the magnitude 7 is the lower limit of destructive earthquakes that cover large areas. Richter and presented in his landmark 1935 paper where he called it the magnitude scale. This was later revised and renamed the local magnitude scale denoted as ml or m l.
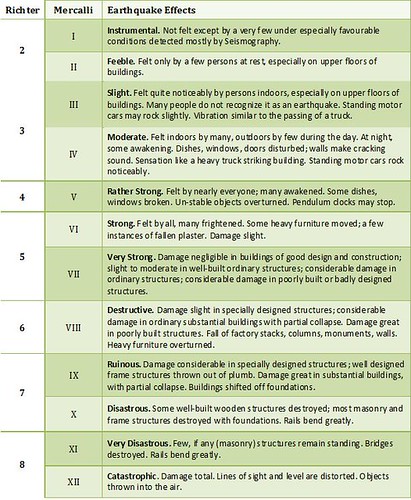
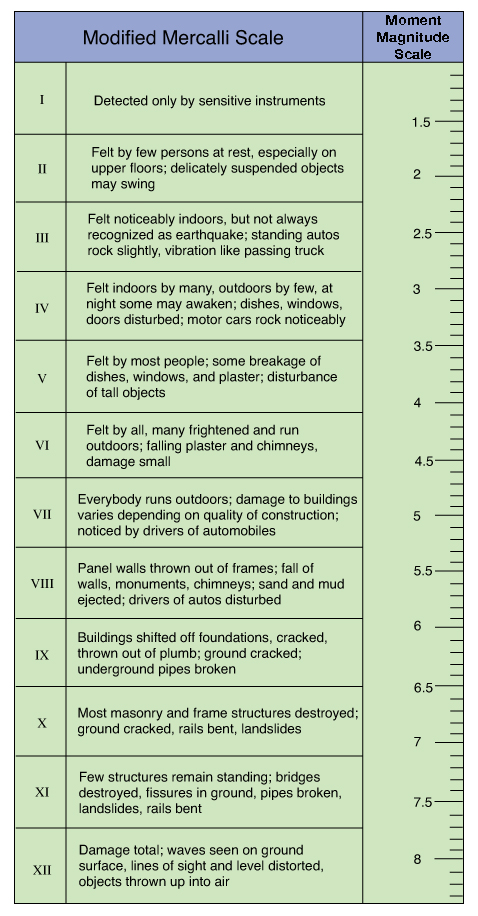
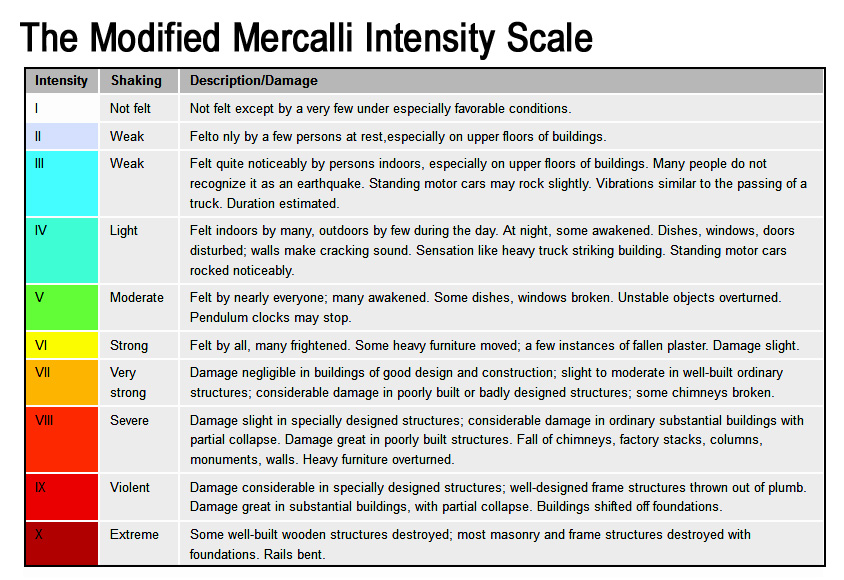
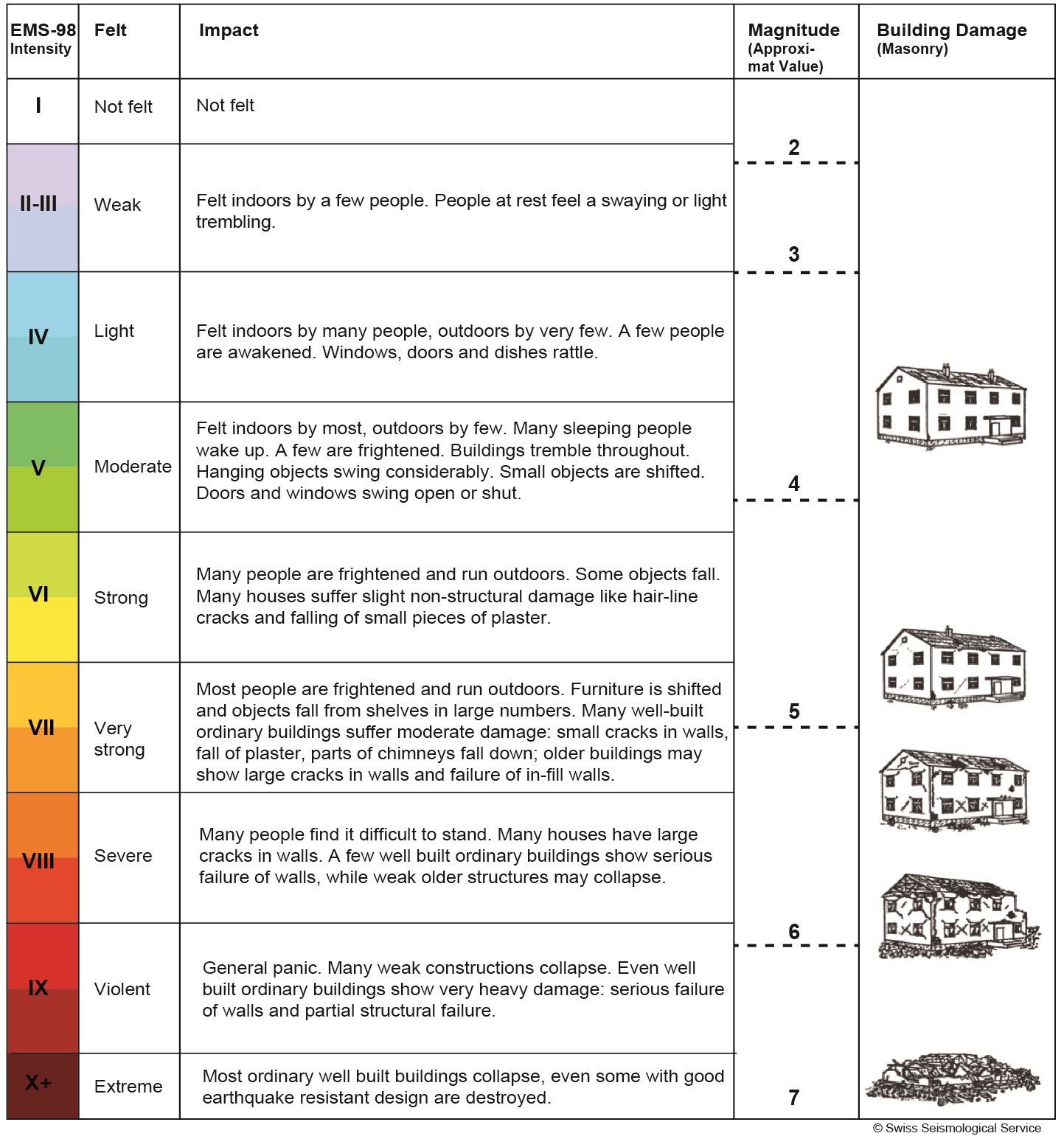
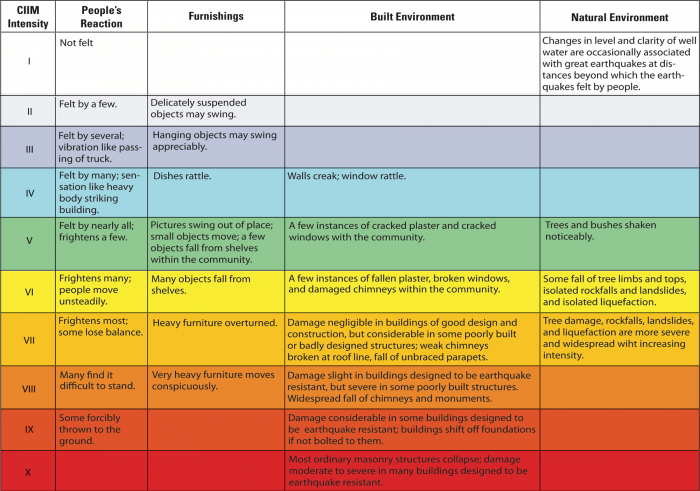
The types and nature of these waves are described in the section seismic waves because the size of earthquakes varies enormously it is necessary for purposes of comparison to compress the range of wave amplitudes. That is the wave amplitude in a level 6 earthquake is 10 times greater than in a level 5 earthquake and the amplitude increases 100 times between a level 7 earthquake and a level 9 earthquake. The mercalli scale measures the intensity of an earthquake by quantifying the effects of an earthquake on the earth s surface.
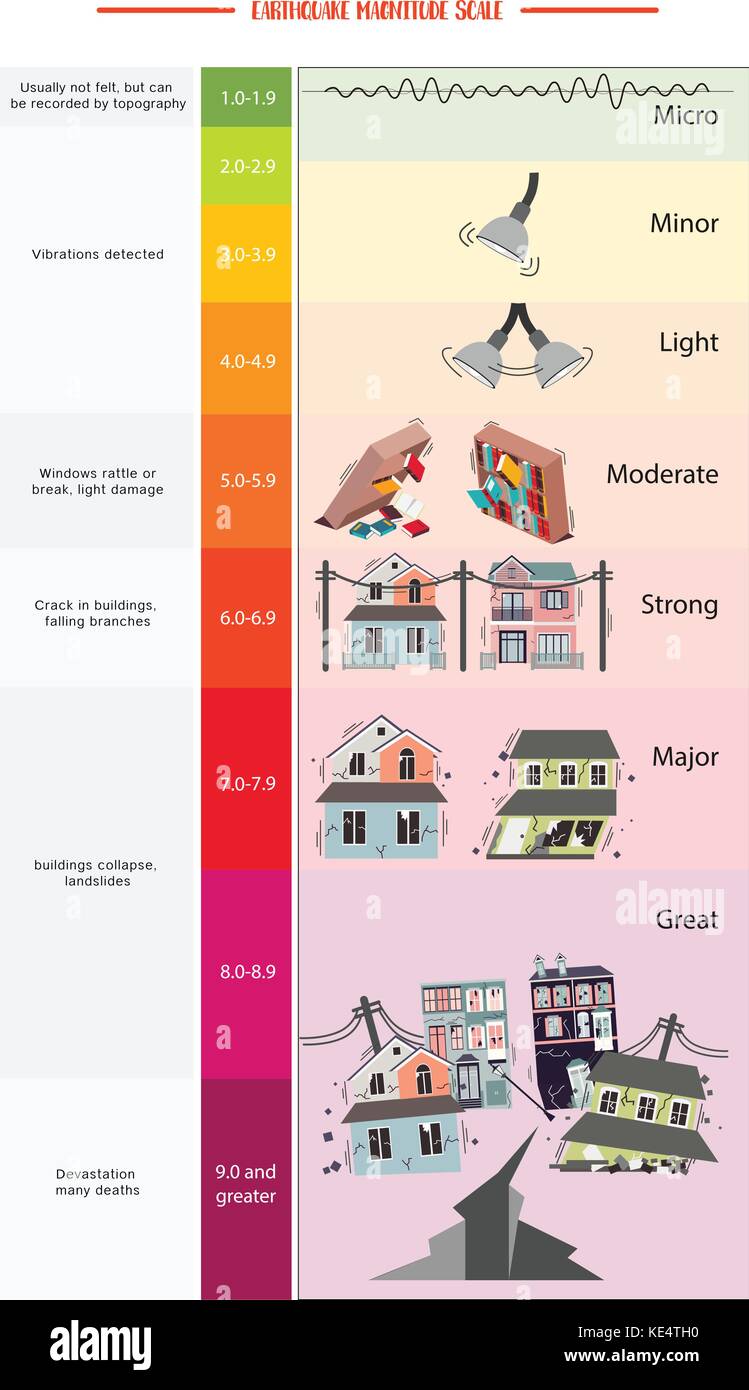
The richter scale measures the magnitude of an earthquake how powerful it is. Seismic magnitude scales are used to describe the overall strength or size of an earthquake these are distinguished from seismic intensity scales that categorize the intensity or severity of ground shaking quaking caused by an earthquake at a given location. Usually not felt but can be recorded by seismograph.
The idea of a logarithmic earthquake magnitude scale was first developed by charles richter in the 1930 s for measuring the size of earthquakes occurring in southern california using relatively high frequency data from nearby seismograph stations. Richter and beno gutenberg. Richter scale widely used quantitative measure of an earthquake s magnitude size devised in 1935 by american seismologists charles f.
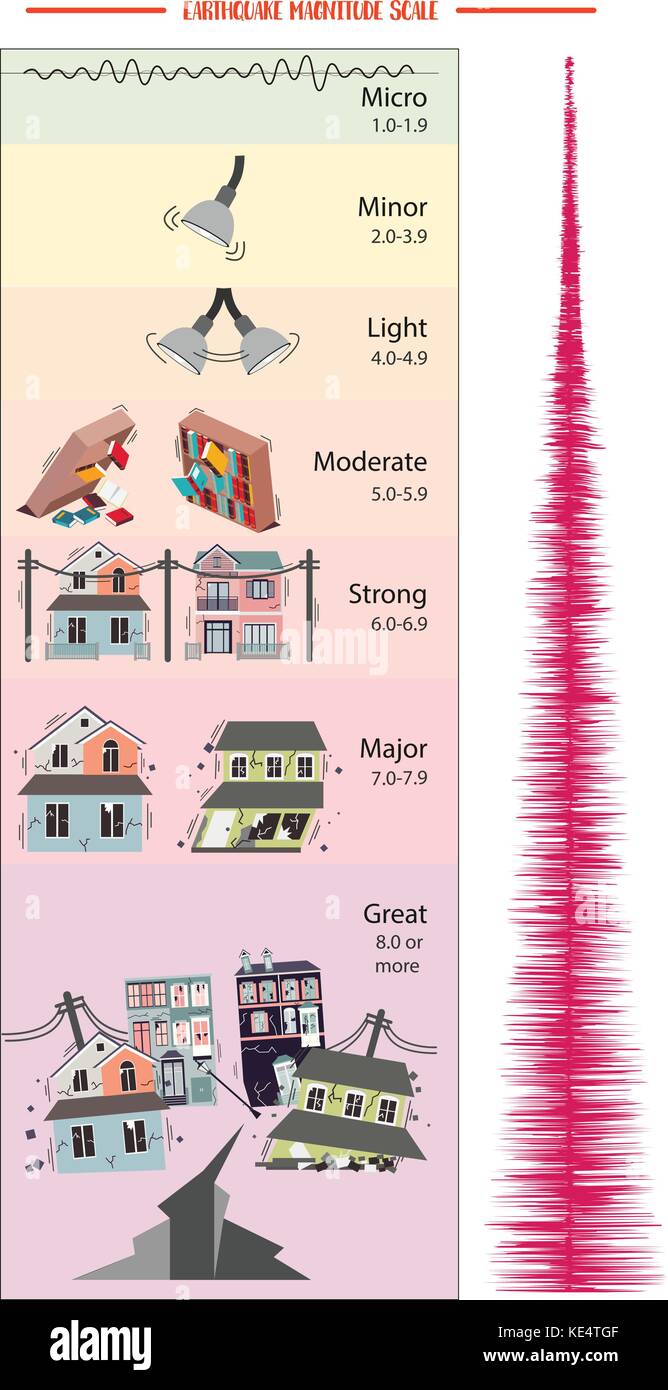
Estimated number each year. Because of various shortcomings of the m l scale most. Based on human reactions natural objects and man made structures the mercalli scale rates earthquakes on a scale of 1 to 12 with 1 denoting that nothing was felt and 12 denoting total destruction.
It is measured using a machine called a.