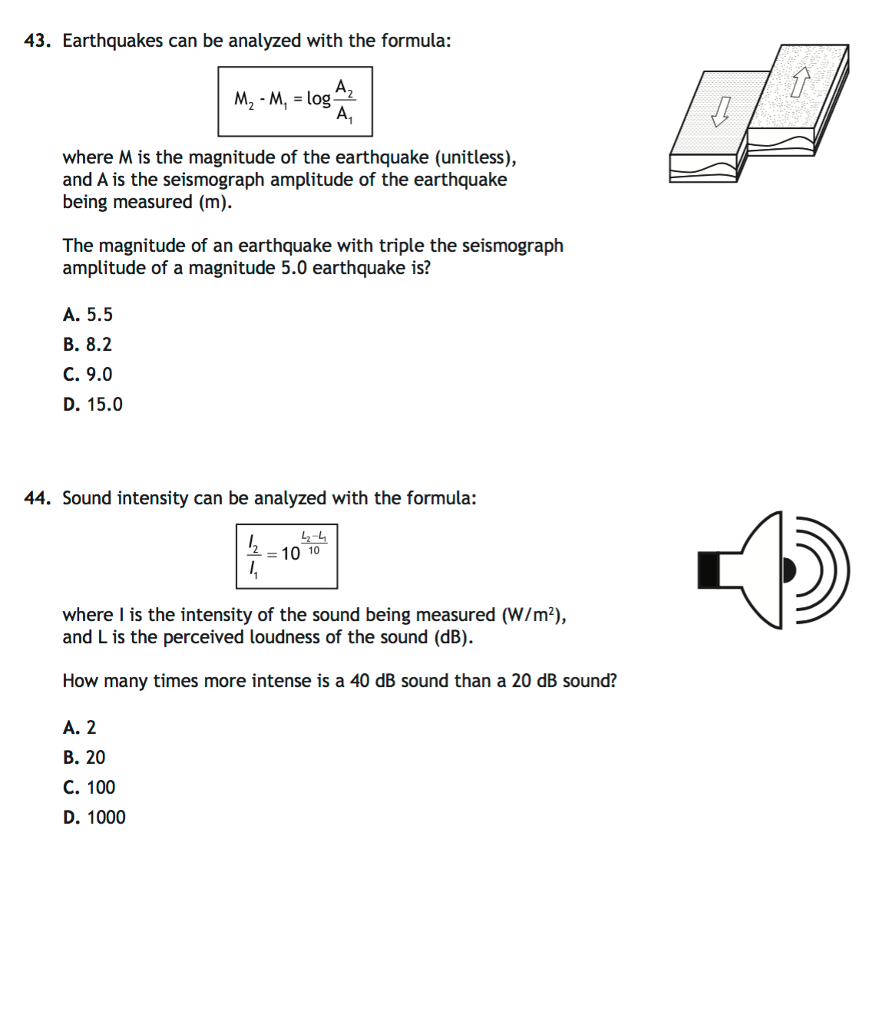
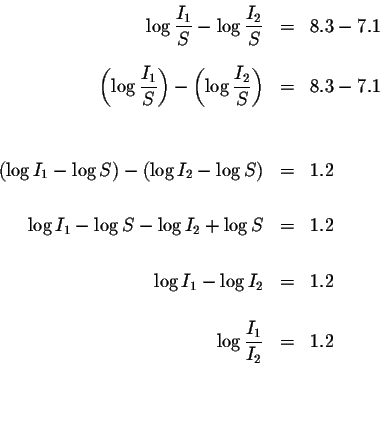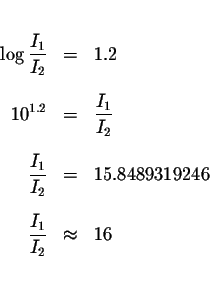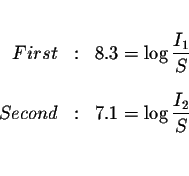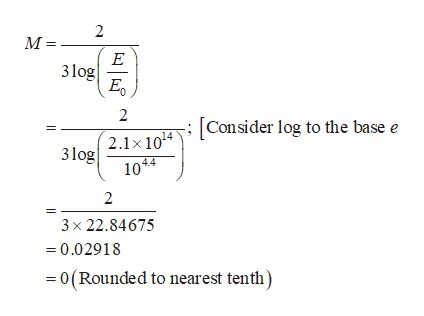Earthquake Magnitude Formula

Where a is the maximum excursion of the wood anderson seismograph the.
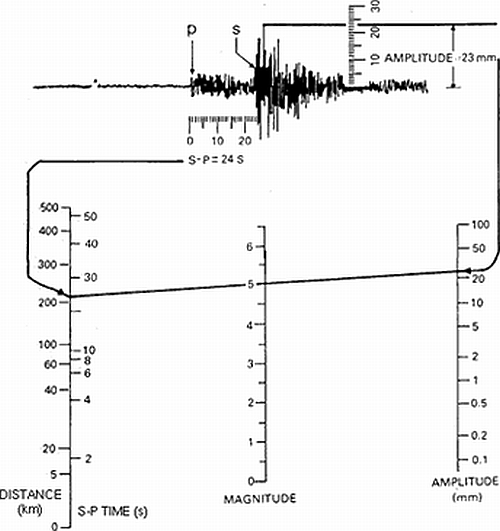
Earthquake magnitude formula. The original formula is. Mb log a t σ d h where a is the maximum amplitude in micrometres of the p waves measured at period t generally about one second and σ is a calibration term in the range 6 8 that depends on distance from the event d and depth of. Early in the century the earthquake in san francisco registered 8 3 on the richter scale.
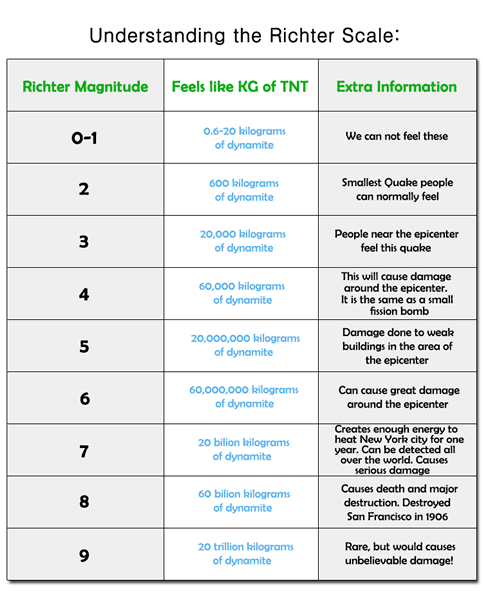
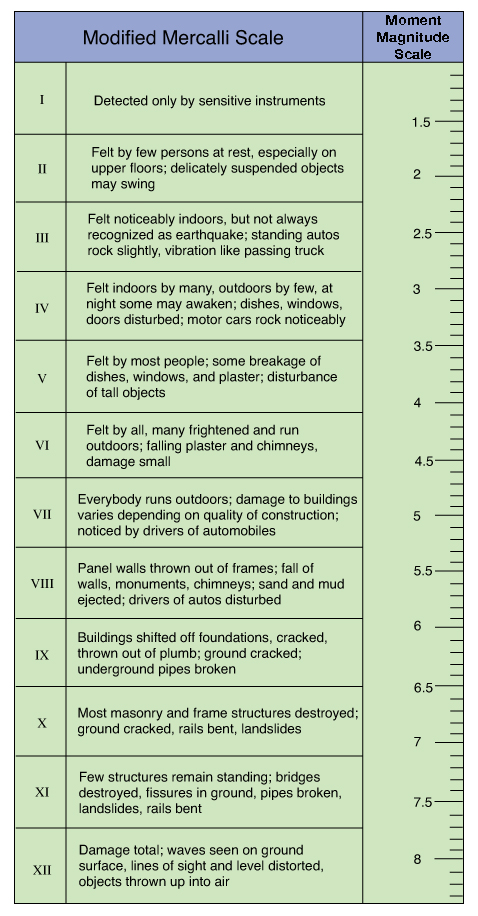
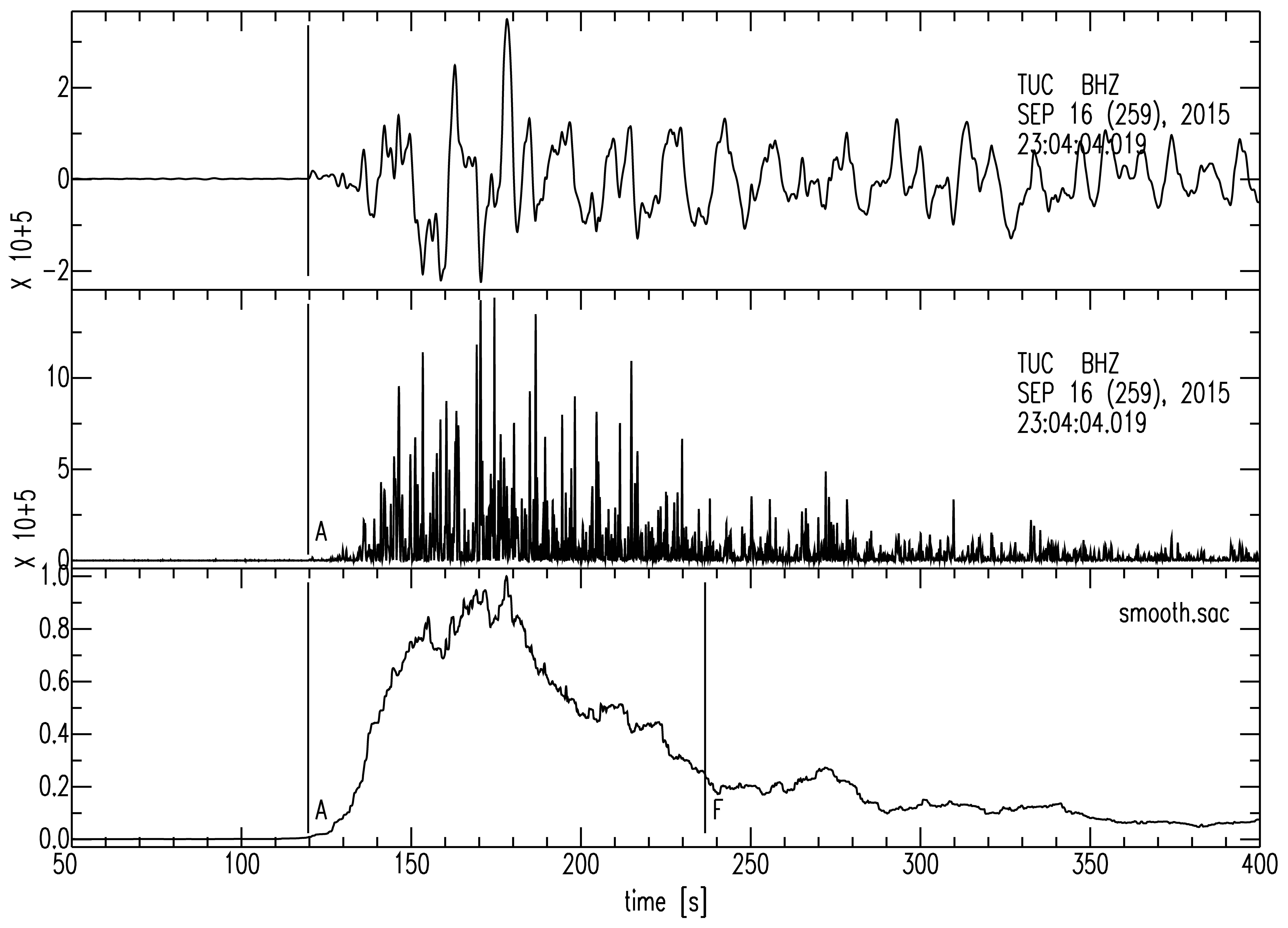
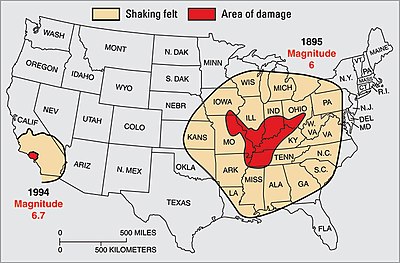
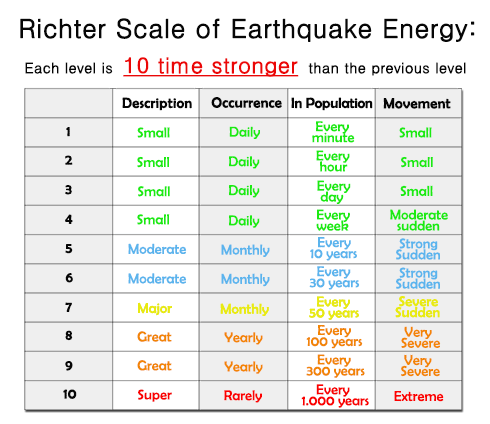
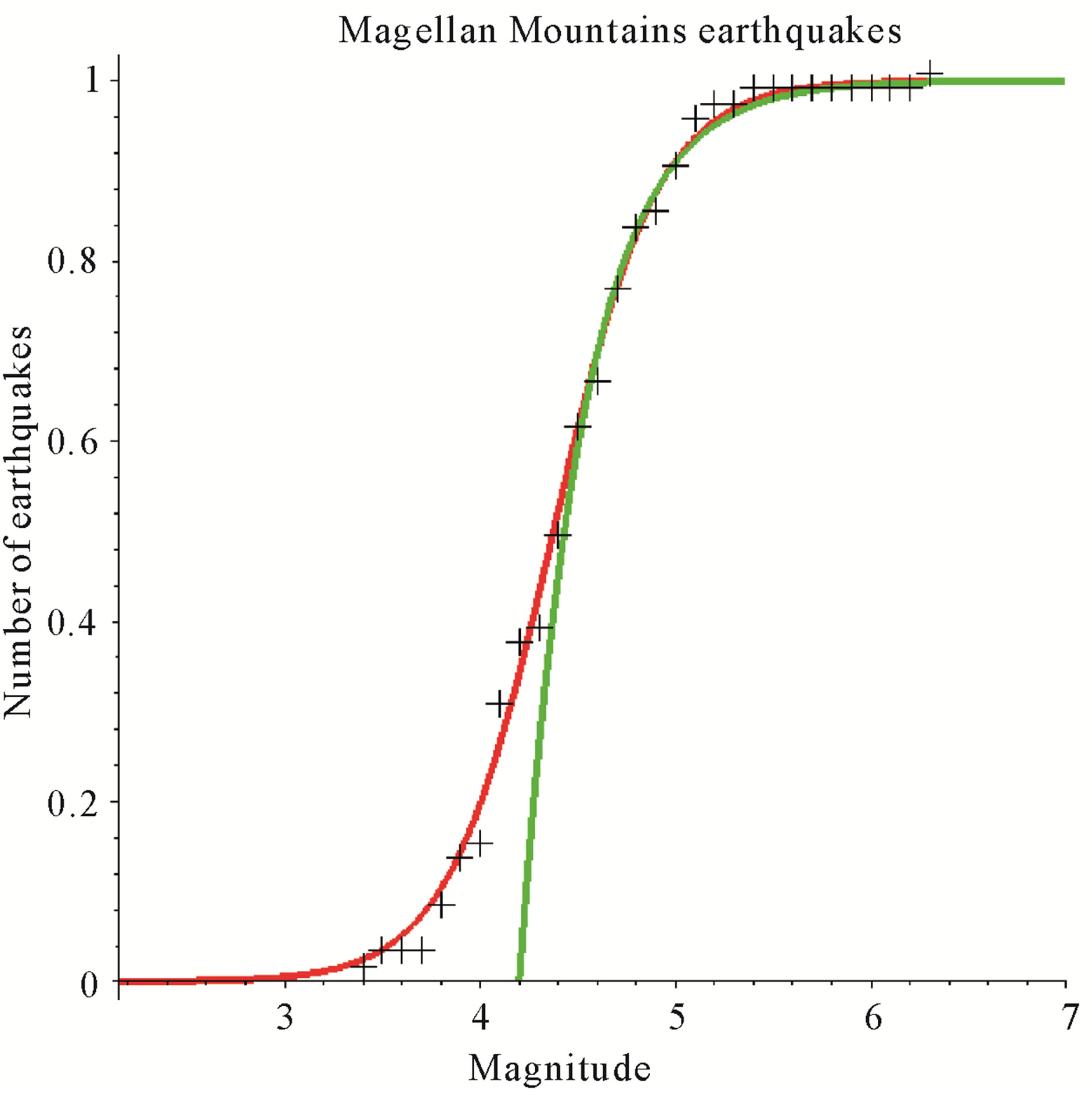
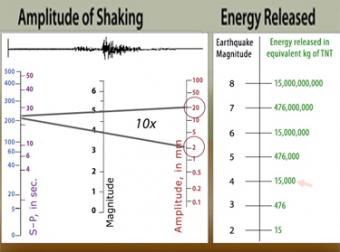
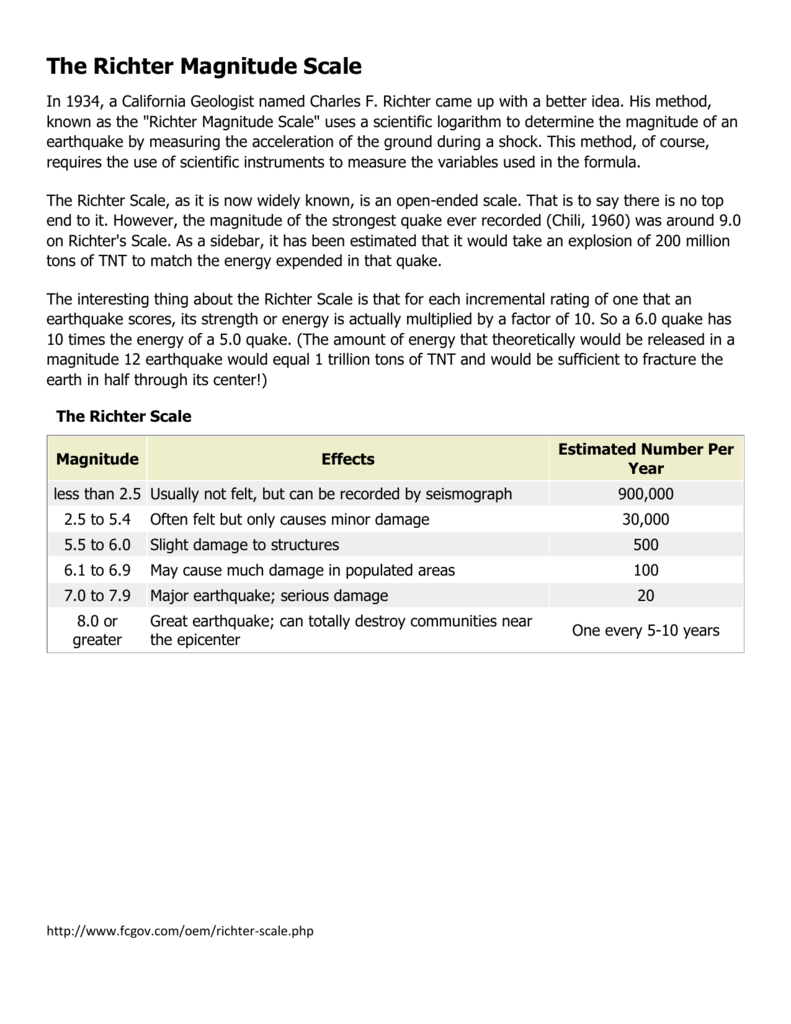
The types and nature of these waves are described in the section seismic waves because the size of earthquakes varies enormously it is necessary for purposes of comparison to compress the. Earthquake magnitude is a measure of the size or amplitude of the seismic waves generated by an earthquake source and recorded by seismographs. Since this is a logarithmic formula each number that represents the magnitude of an earthquake increases tenfold in measured amplitude with an increase in the whole number.
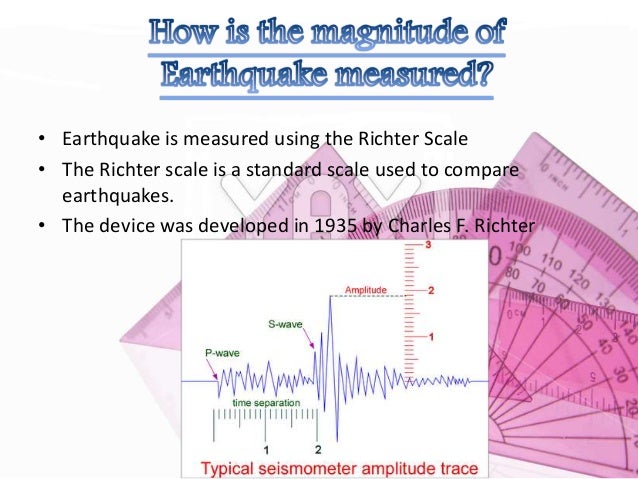
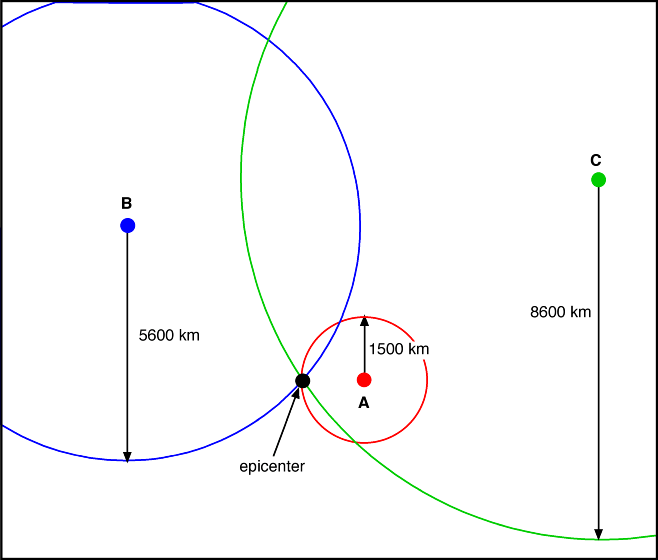
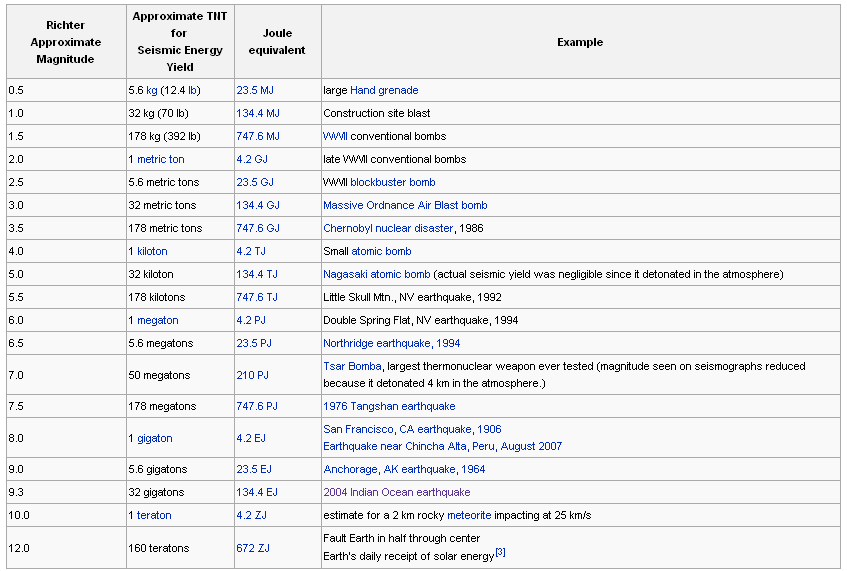
Earthquake earthquake earthquake magnitude. In the same year another earthquake was recorded in south america that was four. The richter magnitude of an earthquake is determined from the logarithm of the amplitude of waves recorded by seismographs adjustments are included to compensate for the variation in the distance between the various seismographs and the epicenter of the earthquake.
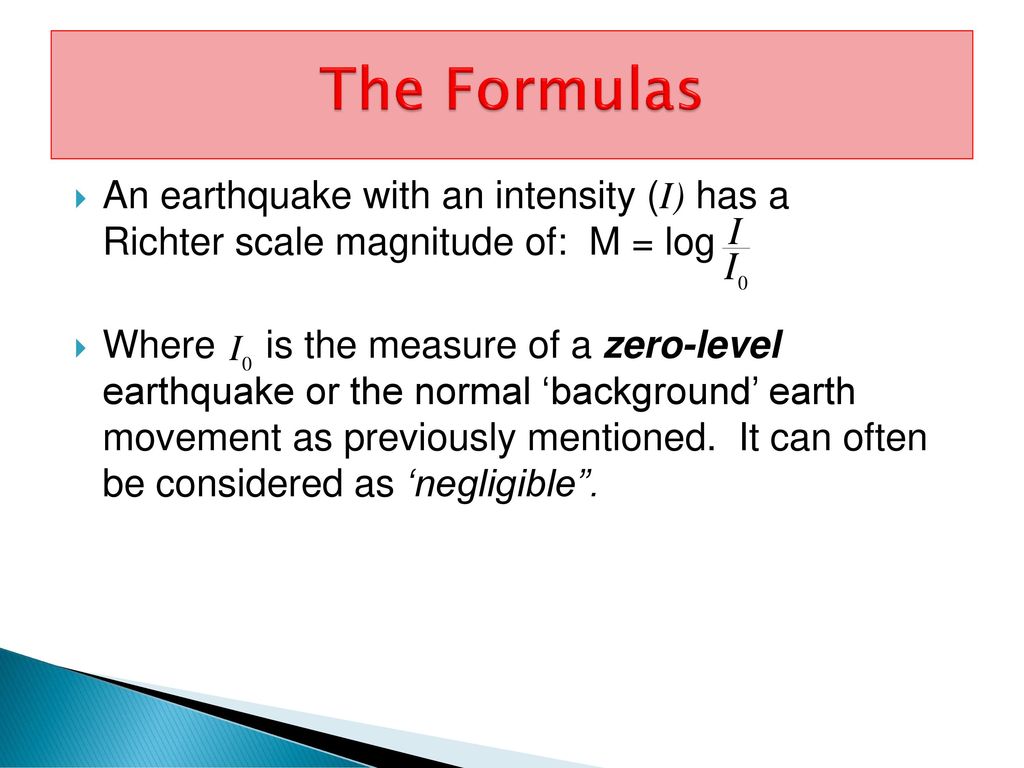
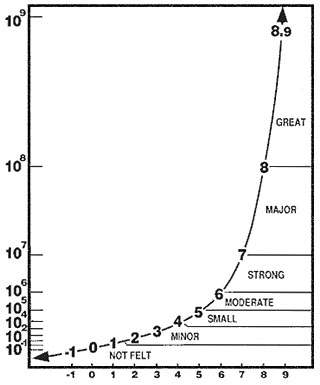
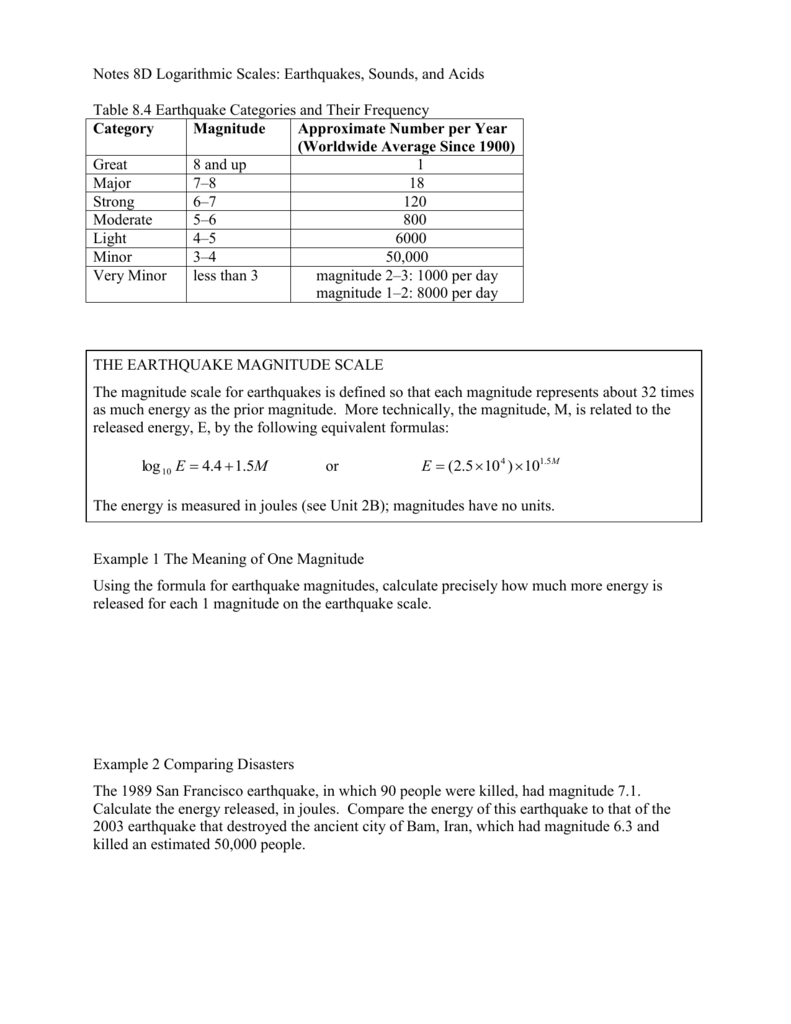
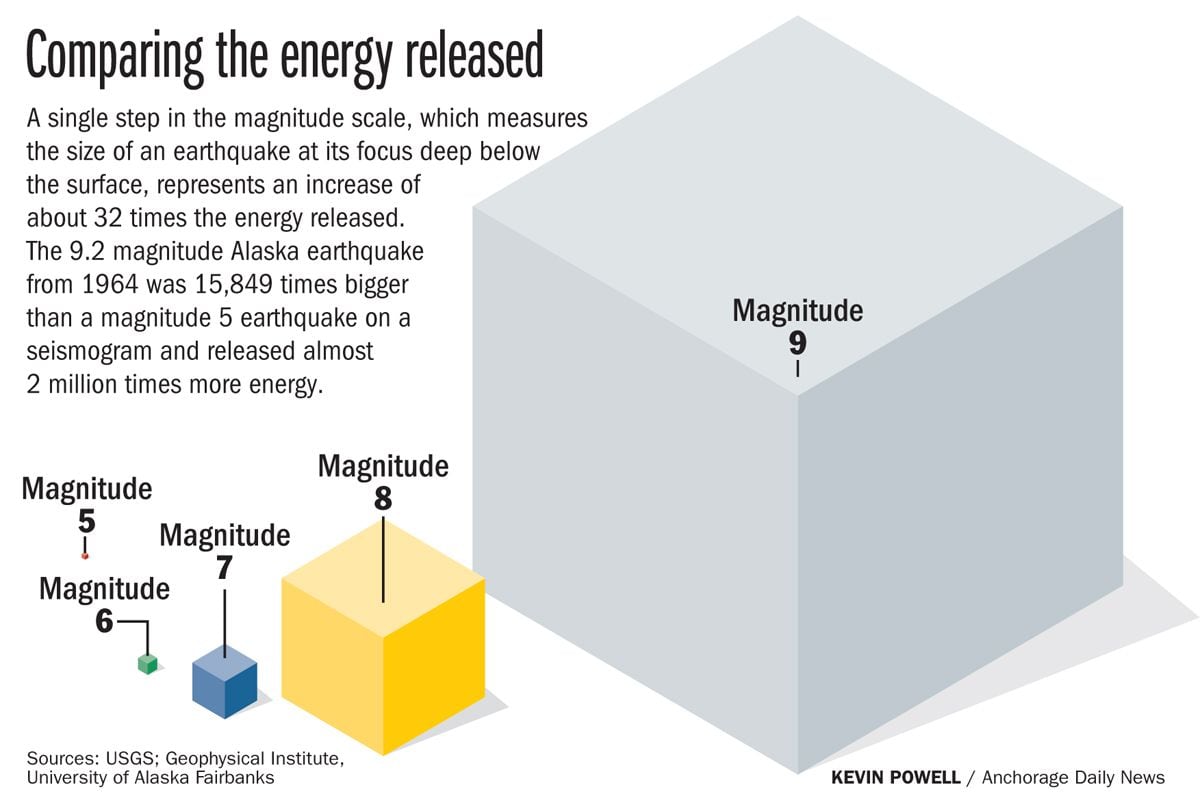
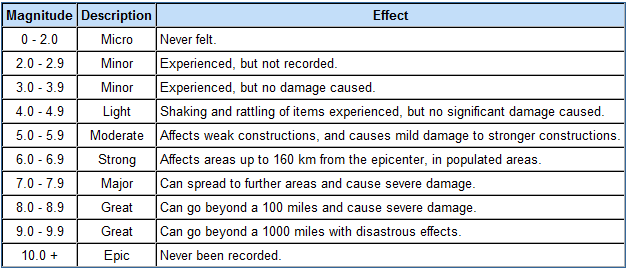
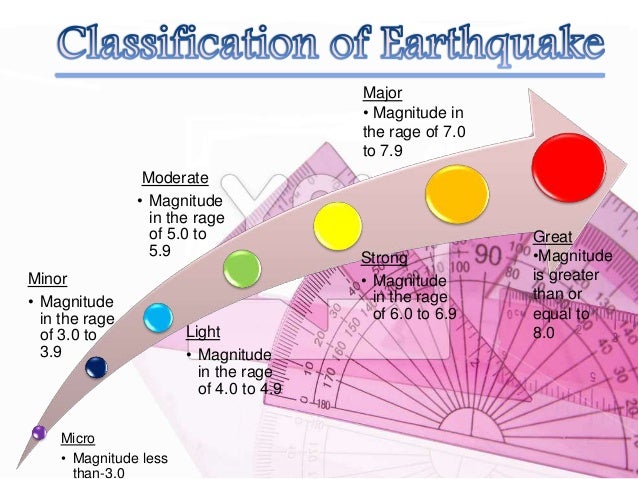
The largest earthquakes in historic times have been of magnitude slightly over 9 although there is no limit to the possible magnitude. The formula m log i s determines the magnitude of an earthquake where i is the intensity of the earthquake and s is the intensity of a standard earthquake how many times stronger is an earthquake with a magnitude of 8 than an earthquake with a magnitude of 6. An earthquake of magnitude 7 is times strong than an earthquake of magnitude 5.
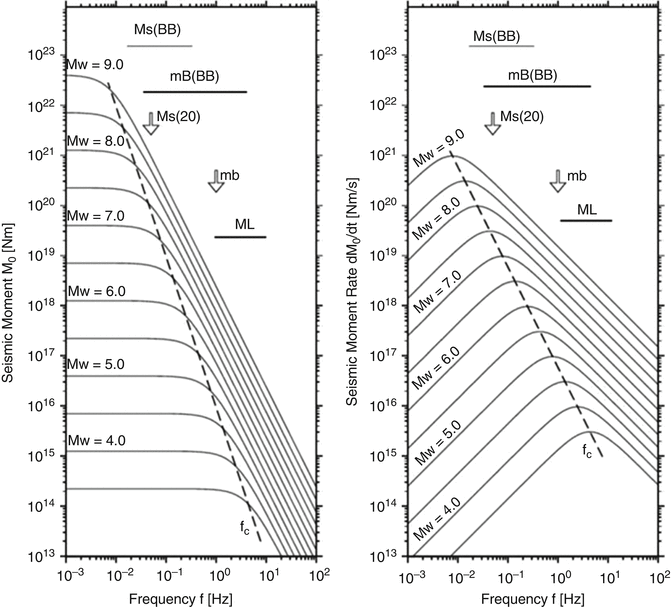
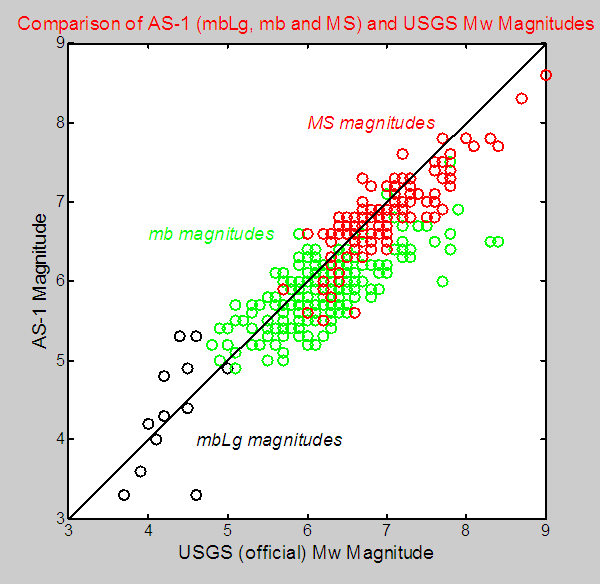
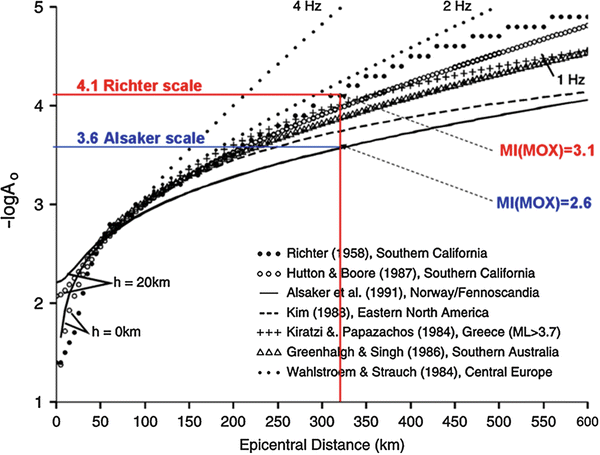
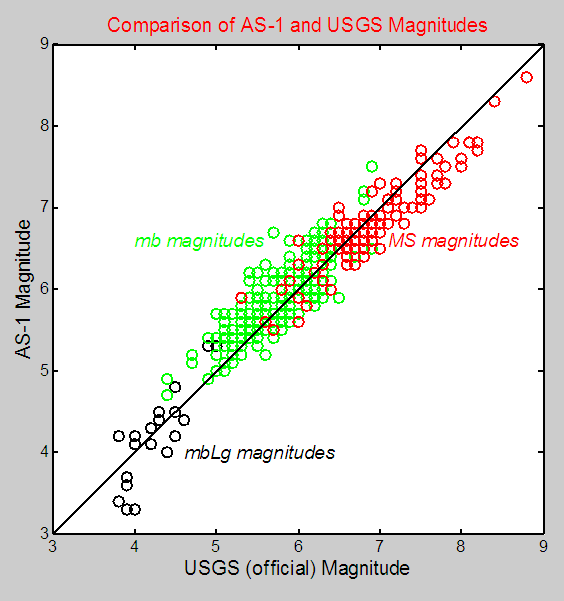
For earthquakes measured at distances greater than 600 km magnitude can be estimated from the formula. The main reason why the moment magnitude scale is the most reliable method of calculating the relative size of large earthquakes is that its underlying calculation process avoids the problem of magnitude saturation because it is based on measurements of an earthquake s total energy. For instance an earthquake measuring 7 0 is 10 times more powerful than one measuring 6 0.
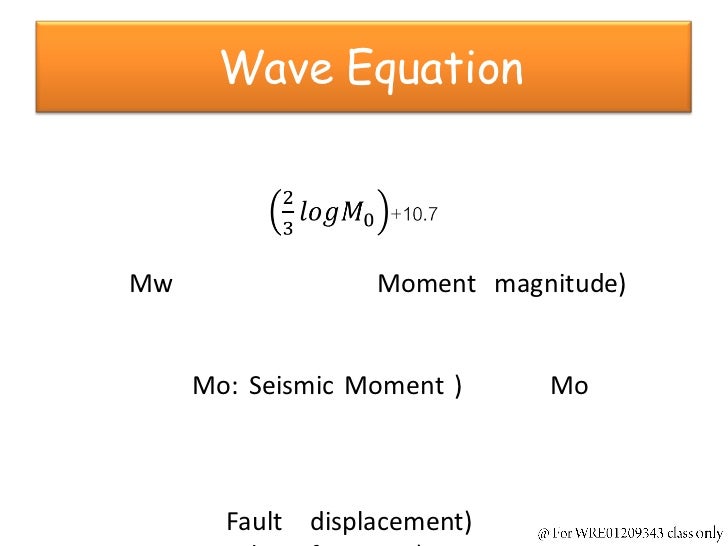
M w 2 3log m 0 10 7. However since the energy magnitude and moment magnitude measure two different properties of the earthquake their values are not the same. The original richter scale formula that is used to calculate the magnitude of any earthquake is as follows.
The most recent large earthquake of magnitude 9 0 or larger was a 9 0 magnitude earthquake in japan in 2011 as of march 2011 and it was the largest japanese earthquake since records began. Magnitude saturation is the tendency for earthquake.